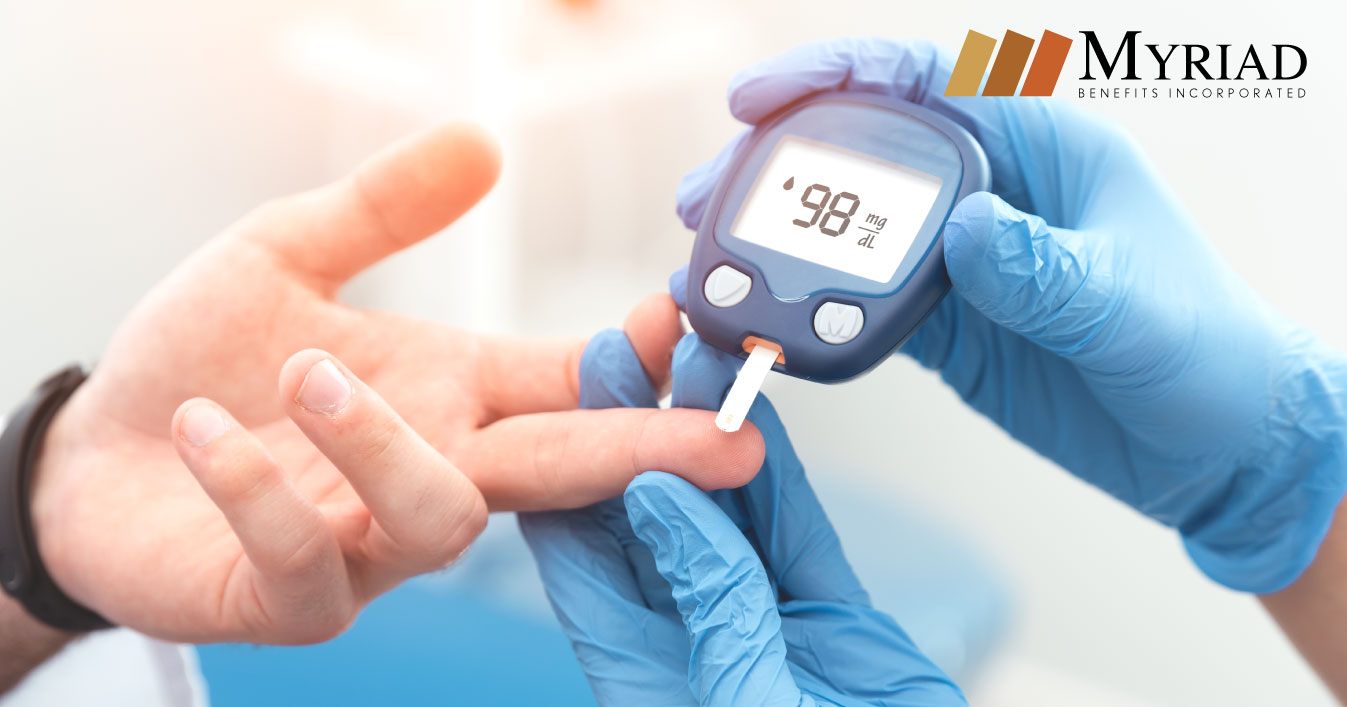
Prediabetes is a blood sugar level that is higher than normal, but not high enough for the diagnosis of diabetes. You can have prediabetes for years without having any symptoms; and detected when serious health problems appear. When you have prediabetes, your body cells do not respond to insulin. The pancreas begins to produce more insulin, but cannot keep up, resulting in high blood sugar levels. In long term, this condition can result in type 2 diabetes.
Find out if you are at risk for prediabetes by identifying the following factors presented by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Being overweight
- Being 45 years or older
- Having a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes
- Being physically active less than 3 times a week
- Ever having gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) or giving birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 ponds
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome
- Being Hispanic/Latino, African American, Indian American, Asian American, or Alaska Native.
Prediabetes can be prevented or reversed by making lifestyle changes such as:
- Do physical activity regularly (30 minutes 5 days a week).
- Keep a healthy weight
- Eat more fruits and vegetables
- Drink more water and less sugary drinks
- Prepared food in a healthier way, with less fat
Talk to your doctor about having your blood sugar levels checked. Stay informed about diabetes. Remember that healthy eating, regular physical activity, the correct use of medications, and regular tests ordered by your doctor allow you to treat diabetes so that complications can be prevented, delayed, and treated.
By: Tania Mangual-Monzón, MS